SEO or keyword cannibalization, currently, can have very negative effects on the search engine positioning strategies of your website or e-commerce site. Why is this topic so important? Search engines and their algorithms are constantly evolving and trying to get closer to relative perfection every day.
This means that they want to offer the most relevant content and with the highest possible quality, that is, the result that responds 100% to the information or consumption needs of their users.
These developments are catching those domains by surprise, as they are not regularly interested in optimising their pages, and now present On-Page SEO problems that can affect their good organic visibility.
And one of these problems, the one that will make your efforts to generate quality content for the user and for Google be in vain, is the cannibalization of keywords… a topic that I will develop in depth today.
Therefore, this time I not only want to show you what keyword cannibalization is, but I would also like to explain the negative effects it causes. But that’s not all, because you will also learn how to detect this problem and, therefore, give it the most effective solution, depending on the type of website you have.
What is keyword Cannibalization?
The keyword cannibalization is a concept that, in the technical jargon of SEO, refers to the situation in which we intend to position ourselves in the SERP with different URLs from our website for the same search intention.
Another simple way of explaining it could be: SEO cannibalization is when you compete against yourself, and by wanting to position more than one piece of content, you will be dividing your forces (therefore, you reduce effectiveness and confuse Google and your users).
From this definition, you should also pay special attention to the fact that I mentioned “for the same search intention”, which means that this topic goes beyond just wanting to position yourself with two URLs for the same keyword.
This is because it may be the case that the Keywords that we try to position are relatively different, but the search intention or “query” of these is the same.
Why Does this Competition Between Pages Occur with the Cannibalization of Keywords?
This problem can be caused by a bad SEO Positioning strategy, as well as by little or poor planning of your content. But, outside of the merely technical section, why not? It can also be due to a simple oversight.
This is a very common problem, and almost no one gets rid of it on the Internet. Whether you are an e-commerce site with thousands of products, a news site that generates a large amount of information, or a business with a simple corporate blog, this SEO cannibalization may be affecting you, too.
So, for any type of website that wants to avoid losing authority, it is vitally important to take into account the pages with which they try to attack each of their users’ search intentions, the internal linking strategies and the entire architecture of the information they have.
In the case of a blog, it would be best not to touch on commercial search intent themes, so as not to compete with the sales section of the website or eCommerce, and to have a well-organised editorial calendar, in which to keep exhaustive control. of the themes that have already been touched on.
Be that as it may, if you think about it coldly, there is no point in launching 2 pieces of content to try to rank for the same keyword or, better said, the same search intent, when they could be addressed on a single page or in a single article, right?
Sometimes, especially in niches of a very specific topic, this cannibalization has also been taking place because they are dealing with the same topic from different angles in different content.
Remember, not by talking about the same thing will you position yourself better; on the contrary, the effect achieved will be just the opposite.
Also Read: AI-Powered PPC Software Tools for In-House Marketing Teams
How does SEO Cannibalization Harm your Web Positioning?
Some of the effects produced by the cannibalization of keywords are the following:
Your authority falls inevitably in the face of the search engine
As with duplicate content, this is not a factor for which Google will directly penalise you. What the search engine does here is lower the quality and authority of your pages, thus losing positions in the search results to your competitors.
In short, all that competition between your own URLs that I have been explaining to you up to here causes your strength to be divided or reduced, negatively affecting your ranking in the SERP and, therefore, your organic visibility.
Instead of having a well-positioned page, with a high CTR and a significant user rating, you have several URLs with almost no relevance, and each one offers possibly incomplete information.
You confuse the search engine
By dividing the authority between different pages that fight to position the same keyword, you are making the search engine not know which one is truly important to you or the one that has more valuable content for the user.
Furthermore, all these contents are really responding to the same intention, and the new algorithms want to adjust the response with the greatest possible certainty and with the greatest relevance to what the user has requested.
In this way, you create a kind of uncertainty about which one to choose, a choice for which the search engine is not prepared to answer on its own… opting for pages of your competitors, URLs to which it attributes more strength and reliability.
In the best of cases, it will be able to present some of your pages in more or less relevant positions, although it will never do so in the place that they might deserve.
You confuse the user.
If the search engine offers several of your pages in the SERP, they may not present the complete information that the user was looking for, causing a bounce that will also affect your SEO.
This reveals to the search engine, undoubtedly, that your content is not relevant enough for that query or query. The user’s perception of the quality of your page is, therefore, very bad, since this does not help at all to offer an optimal user experience.
This bad image of your site will presuppose a lack of ideas, imagination and creativity. In short, you will give an impression of a lack of quality and competence, especially in the case of services that require deep knowledge and high professionalism.
You are indexing pages that are unnecessary.
In this way, in turn, you make search engines uselessly crawl URLs from your domain, thereby wasting Google’s time. This reason can be better understood once you understand exactly what the Crawl Budget is.
Perhaps in cases of moderately “small” blogs, this factor is not so important, since it will not have a large number of indexed URLs.
However, imagine the case of an e-commerce with thousands of references, between product sheets, URLs of colour variants of the same product, sales pages, catalogues, etc.
SEO cannibalization hinders Link Building
With how difficult it is to do Link Building or gain quality inbound links, by cannibalizing themes, you will almost certainly have them scattered throughout different places on your site.
For example, if you have 2 or 3 pages that talk about the same topic, how will others know which URL they should link to from one of their content?
Which of them will be the main page or the one with really relevant information? Based on this, they will make a random decision, and the links they implement to your website will be divided among several pages.
Also Read: How to Utilise Long-Tail Keywords for SEO
How to identify if my website has SEO or Keyword Cannibalization?
In general, I can tell you that normally it is not very difficult to detect the keyword cannibalization. This problem could be detected in a thorough SEO audit of our website.
Although, as you will see below, thanks to these 3 simple methods, you will get very clear and precise information.
Using the internal search engine of your website
This is a very basic and simple method, consisting only of writing the main keyword or idea of the contents that you suspect are cannibalizing each other.
The result of this action will give you all the content on your site that includes it. It is precisely there that you should intuit if there is content that responds to the same search intention.
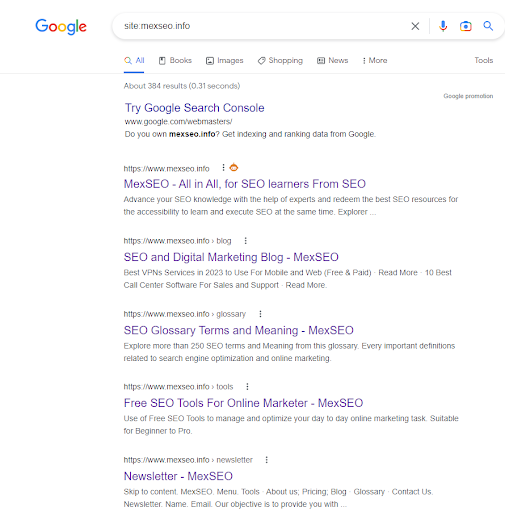
2º Use the command “SITE:”
Among the basic functionalities of Google, different commands help you analyse a website. For example, with SITE, you can detect your indexed pages:
site:mexseo.info
And if we add or add a key term or phrase in quotes to that search, we will also see the content within that domain:
site:mexseo.info + “SEO”
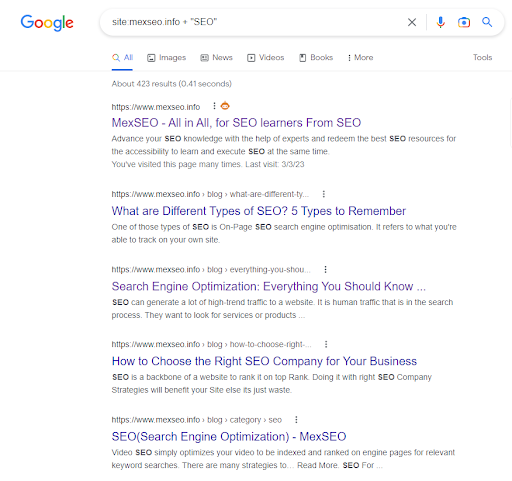
The result will give you a SERP made up of all the ULRs of that domain that are indexed and that have that Keyword in common, that is, those that are fighting each other for a place in the same search.
It is now where, again at your discretion, you must carefully analyse whether these URLs have content that could satisfy the same user need.
3º Through your Search Console
If you have your website registered on the Google Search Console platform, you can also detect keyword cannibalization.
To do this, you must follow these simple steps:
- Enter your property and in the section « Search traffic > Search analytics «.
- Within the list of keywords that are shown below the graph, click on the one that you intend to analyze in search of cannibalizations.
- From here, turn on the “ Pages ” option. This will show you which URL’s that keyword is ranking for.
- In case it is positioning for 2 or more different pages of your website, you will have SEO cannibalization.
How to correct SEO cannibalization on my website or e-commerce site?
Depending on the volume and size of your Internet domain, as well as the amount of content that you have generated throughout the life of your site, you will have to use one method or another of those that I propose below:
Create a single content for each Keyword
It is best to plan everything and create a single page with all the necessary information for the user, that is, a single URL for each keyword.
301 redirect (unify all URLs into one)
If you already have carnivals, a possible solution could be to analyse those URLs with some competitive research tool, such as SEMrush or Ahrefs, to see which one has more organic strength.
By this I mean that you must thoroughly analyse which of them has the highest authority, the most incoming links, the most positioned keywords, etc.
There could also be a simpler case, whereby you verify that one of them does not have backlinks or ranked keywords. Here, you would already know very easily which of them to “sacrifice”.
Then, from there, we would compose a single content with all the complete information within the URL with more organic force, adding to it the most notable of the others that we are going to discard. But…
So what do I do with the other URLs?
With that being said, the idea of simply deleting them out of hand might come to mind. I must remind you that, although they produce SEO cannibalization, they may receive internal links from other content on our website, have been shared on social networks, etc.
Therefore, if we eliminate them, anyone who tries to enter will get a ” 404 Error ” as a result. Given this, I will give you a solution:
301 redirect
If we redirect them to the content that we have taken as “reference” for that keyword or search intention, each time the user tries to enter the redirected content, they will go to the main URL.
In this way, users will experience a better response to what they were looking for, as the latter has all the information they were looking for in a single piece of content.
And in turn, this UX improvement means that we are giving positive signals to Google, so that it takes into consideration the action that we have carried out in organic terms.
In addition, the redirected URL will transfer its authority to the destination one and make it more powerful. Despite these advantages, on the contrary, you should also assess that you will lose all the comments you had from your readers in the content that “disappears”. Like everything, it also has its downsides!
Internal linking
A somewhat “light” measure by itself, not to solve the keyword cannibalization, but to “make up” for it and make Google see which of the 2 URLs is the most relevant is with the internal linking from one to the other.
This basically consists of launching a “dofollow” link with the exact anchor text from the “less relevant” or worst-positioned content to the most powerful and best-quality URL.
My personal advice is that we remove said link as soon as possible. For example, if you usually introduce your articles with a lead or previous introduction, this would be the ideal moment.
Why would we integrate it at first?
Very simple: logically, if Google robots begin to scan the contents from the beginning to the end, the sooner you see this backlink, the sooner you will have signs that the post we linked to is more important to us for that keyword.
As I mentioned before, this is not a super effective solution to eliminate cannibalization from our Web, but it is a fairly simple way to try to lead the way to the search engine.
In addition, it is ideal for cases in which you manage a client’s blog, which allows you to generate and publish content, but does not allow you to have access to certain technical sections of it, so it would be impossible for you to carry out a redirection.
Also Read: From Chatbots to AI Agents: How AI Is Transforming SEO
Canonical
Basically, the canonical consists of making a “suggestion” to Google that, when faced with several similar content or that in theory should rank for the same keyword (or search intent), there is one that is the most relevant of all.
This alternative, however, has the drawback that it does not transfer authority to the URL that we indicate as relevant for that search intention, contrary to what happens with 301 redirects.
In addition, the use of canonicals is nothing more than a “suggestion” that we make to the search engine, which it can perfectly ignore.
Why is this solution more recommended for an eCommerce than for a blog?
This is an alternative more used in online stores than in blogs, since in an eCommerce, the case of having cannibalization or duplicate content for terms such as:
- 1st «Red sports shoes»
- 2nd “Green sneakers”
- 3º «White sports shoes»
As you can imagine, we could add a long list of URLs, as many as the colours we present in our store. Therefore, the main keyword in our case would always be “sneakers”, with the only exception being colour, right?
This is where this “suggestion” makes sense, since taking the product sheet of red sneakers as the canonical URL, it makes no sense to redirect the sheets of the other colours to red, since in the user’s eyes, the other colours will not exist, because they will always end up in the destination URL that we have marked.
Sometimes, if we take the previous one as an example, it is almost inevitable that there may be dozens, or even hundreds of references that point to an identical Keyword.
It is evident that you cannot change this and that you cannot put all the product variants in the same file either. Canonicalization can be used, but sometimes it is preferable not to index these product pages in search engines, leaving only the category page.
This is easily achieved by using the “noindex” tag. This way, search engines will ignore these pages and not crawl them, and you can put all your effort into ranking well for the categories.
Conclusion
As a general rule, the Keyword Cannibalization and good positioning do not go together, and this phenomenon seriously affects the obtaining of good positions for your domain in search engines.
You must know how to identify it and detect where you should correct it to improve the ranking of your content, acting on those that are dispensable and promoting those that can offer more relevant content.