In recent years, new positioning elements have emerged, gaining importance in the SEO of any website. One of them is called Core Web Vitals. Surely you do not know what we mean by this term, since it is still relatively unknown. That is why we consider it important to decrypt your keys.
Here you will discover what Core Web Vitals are and how you can apply them to your project to gain relevance and natural positioning.
What are Core Web Vitals?
Core Web Vitals is the name given to the new unification of metrics. They are part of Google’s Page Experience, which has designed this signal to provide a unified, innovative measurement formula that improves the user experience.
Google has spent years improving the user experience to better adapt to reality and the true search behaviour of Internet users.
However, many webmasters are still very focused on obtaining traffic, without often thinking about the quality that individuals must find on every site they visit if they are well-positioned in the SERPs.
Thus, Google itself has now centralised, thanks to Core Web Vitals, the key metrics that show the true quality of the user experience. For this, we find three unique aspects that we must always take care of:
- LCP: is the payload described in the term Largest Contentful Paint.
- FID: Interactivity with the user is summarised in the term First Input Delay.
- CLS: The visual stability of the web is summed up in the term Cumulative Layout Shift.
These metrics can be monitored on PCs and mobile devices, though only the latter will count in the rankings.
Add that, when looking at the scores, we must be clear that the metrics are evaluated at the 75th percentile across users; therefore, to pass the Core Web Vitals, the recommended minimum scores must exceed 75% of the scores. Visits.
Also Read: Essential Website Optimisation Strategies
What are the Characteristics of the Core Web Vitals?
We have already briefly discussed the three main Core Web Vitals metrics. Now, let’s go into one by one in greater depth to understand how to achieve a good score for our Online projects.
LCP or Largest Contentful Paint
As we mentioned, this metric focuses on the performance of each page’s load. That is, it measures the time it takes to load the main content of your website. Here, we will see the loading times of the featured image, a large paragraph of text, or the main section of your site. That is, it focuses on what is relevant to the user.
Today’s studies show that the largest element of a website is usually the first one users want to see.
Thus, it will be the one that performs the best without affecting the CSS, and it will do so across all kinds of formats, for example, mobile, which is so important for Core Web Vitals, as we have just said.
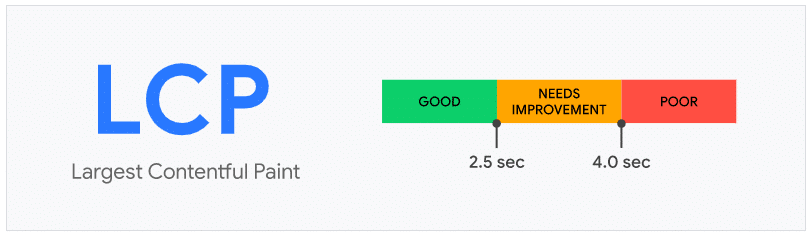
LCP Values
According to Google metrics and scores, for it to be good and reach 75% of page views, it should have a load time of no more than 2.5 seconds. Underneath, you will get a good score. Between 2.5 seconds and 4 seconds, it will go to a score that can be improved. More than 4 seconds is considered bad and detrimental to the site.
Be careful, in this case, the high score indicates that the user waits too long to see the content. Rendering time is excessively high. So, if you have large videos or images on your website that aren’t rendered or are blocked by JavaScript, it’s best to fix them as soon as possible to avoid losing traffic.
FID or First Input Delay
Let’s now look at the second key aspect of the Core Web Vitals metric: FID (First Input Delay). In this case, we observe that it focuses on interactivity and the ease of offering answers from the web itself.
First impressions are considered, with possible delays in event processing evaluated.
In other words, the delay is measured from the first time the user interacts with the site, for example, by clicking on a link or button, and analysing the time that elapses from such a click to the end of the processing. It should also be noted that the FID does not account for interactions such as zooms or displacements. Only the first interaction is considered key in the user experience.
If a web page does not offer user interaction, or that interaction does not occur, the FID will not be informed, so it will not be collected.
The FID is reminiscent of the TTI (Time To Interactive), which measures the time it takes for a page to become interactive. Of course, with the exception that the FID measurement occurs before the web is fully interactive.
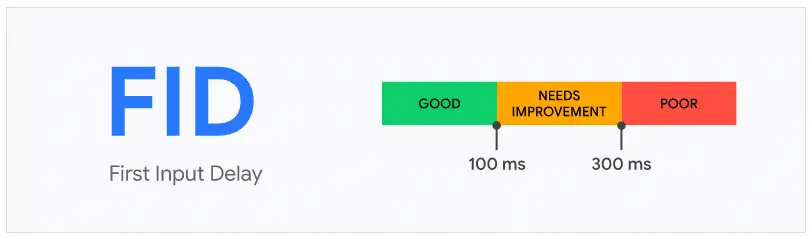
FID values
In this case, getting a good FID score requires having a load time below 100 milliseconds.
When this figure is between 100 and 300 milliseconds, we are informed that it needs improvement; if it exceeds 300 milliseconds, our First Input Delay is bad or very bad and requires immediate action.
CLS or Cumulative Layout Shift
Finally, we go with the third metric, which indicates whether we have a good or bad user experience. In this case, the CLS measures the visual stability of the web page. This parameter will be defined due to an unexpected design change.
For example, let’s say a visible page element suddenly changes size and position, which, by default, will affect the position of all surrounding content. This would be a design change, as we have mentioned.
What to do if a user accidentally clicks the wrong button because late-loading content caused the button to move? You have to act promptly.
Thus, it is convenient to ensure that, while they are loading, the elements of a website remain static. Therefore, when adding all the aforementioned design elements to the CLS, the movement distance of each element and the viewing window affected by the change will be considered.
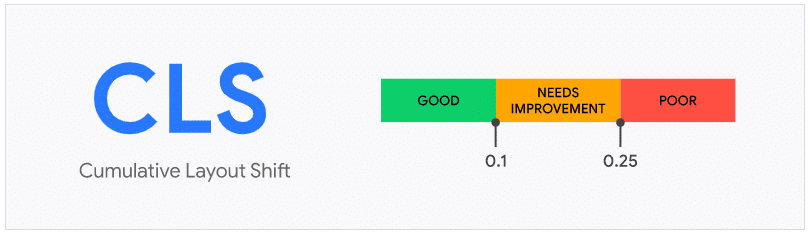
CLS Values
In this case, Google uses the correct punctuation when the time is less than 0.1 seconds. It is necessary to implement improvements when this type increases from 0.1 seconds to 0.25 seconds, and we should consider that we have a bad CLS when it exceeds 0.25 seconds.
But what do these times mean? The content of the web will be completely static during its life cycle, which implies a low score. However, it goes up when the contents are moved. Design elements that increase CLS time include images, dynamically injected content, web fonts that cause unstyled or invisible text, ads, embeds, and undersized iframes.
We must stay up to date on Google’s Core Web Vitals updates. In the case of the CLS metric, there have been changes that penalise sites with low scores.
For example, in apps such as social networks that have been open for a long time, as established, it was considered inappropriate. It happened, for example, with the aforementioned social platforms. Thus, this adaptation improves its measurements and affects more than 50% of websites.
How do the Core Web Vitals affect the SEO of a Website?
Given what has been seen, it is logical to assume that Core Web Vitals significantly affect a site’s natural positioning. That is why it is convenient to use good web design, development, and optimisation practices to increase the score and avoid losing positions in the SERPs.
Among these practices, it is important to keep in mind that cheap web design is unlikely to be internally optimised. Therefore, its initial cost advantages can be detrimental to speed and load optimisation.
It is common that, just as we always optimise websites to increase SEO, we also do it to enhance Core Web Vitals, for example:
- With fast and reliable hosting.
- Enabling the full page cache.
- Deferring JavaScript.
- Minifying the JS and CSS files.
- Optimising the browser caching we use.
- Using the CDN.
- Removing any third-party script that is not necessary.
- Compressing the images well and ensuring they are correctly scaled.
- Lazy loading static content.
- Eliminating all the elements that are too heavy on the web.
- Compressing all the files.
Also Read: Unlocking the Power of Paid Search and SEO Integration for Online Success
Tools to Measure Core Web Vitals
Given the importance of Core Web Vitals in recent times, several effective tools for measuring, analysing, and controlling them have emerged. Among the most important are the following:
Google Search Console
Google Search Console is the main one, since Google itself provides it.
Known as the Field Data tool, it allows for the collection of field data by monitoring real users. Thus, groups of pages can be identified for analysis and problem-solving using the three metrics: CLS, FID, and LCP.
PageSpeed Insights
PageSpeed is an interesting tool for analysing the page’s viability based on loading speed. It is browser-based and helps analyse site performance.
Chrome UX Report
Also known as CruX, it provides a set of publicly accessible data for user experience analysis through the Chrome browser. This helps us analyse the Core Web Vitals metrics.
Web Vitals Chrome Extension
Web Vitals is a Chrome browser extension that lets us accurately measure Core Web Vitals in real time. It is used on the PC desktop and has become a great diagnostic tool.
web.dev
Web.dev is a free tool that makes it easy to run a full audit to assess a site’s true performance. Verified the performance; we found a section of advice on applying progressive improvements to accessibility and web applications.
Lighthouse
We are now using a Lab Data tool that runs tests in controlled environments to analyse potential users and their experiences with the web.
In this case, Lighthouse is a great tool for diagnosis and quality improvement.
WebPageTest.org
Another magnificent Lab Data technique that is free and open source. With WebPageTest.org, it is easy to analyse a website’s performance by measuring page load speeds in a browser.
Performance Panel
Let’s go with one last very simple tool provided by Chrome DevTools, which is also quite easy to use.
Panel performance is measured in incognito mode in Google Chrome and used to assess the user experience for possible undetected or unexpected design changes.
Thus, if visual instabilities affect Core Web Vitals metrics, they can be quickly identified and addressed without significantly affecting site performance.
Also Read: Best Content Optimisation Tools for SEO Beginners
Conclusion
The majority of users, and a good number of inexperienced webmasters or those who do not get informed on time, still do not appreciate the importance of Core Web Vitals.
However, we have just verified their current importance, as Google takes them very seriously in the SERPs. Fortunately, controlling these metrics is easy, as we have a good number of free or low-cost tools, many of which are available online, that help improve final scores.
In short, a good website that can survive on its own requires constant work and full attention. Additionally, if you wish to build a superfast website that surpasses the Core Web Vitals to optimise each element in detail, use PHP benchmarks through Laravel development services.
Now, as part of your SEO work, it is a basic condition that you implement Core Web Vitals to optimise every detail. If you start today, it’s better than starting tomorrow.






